Natural History
Flora and Fauna of the Bahamas
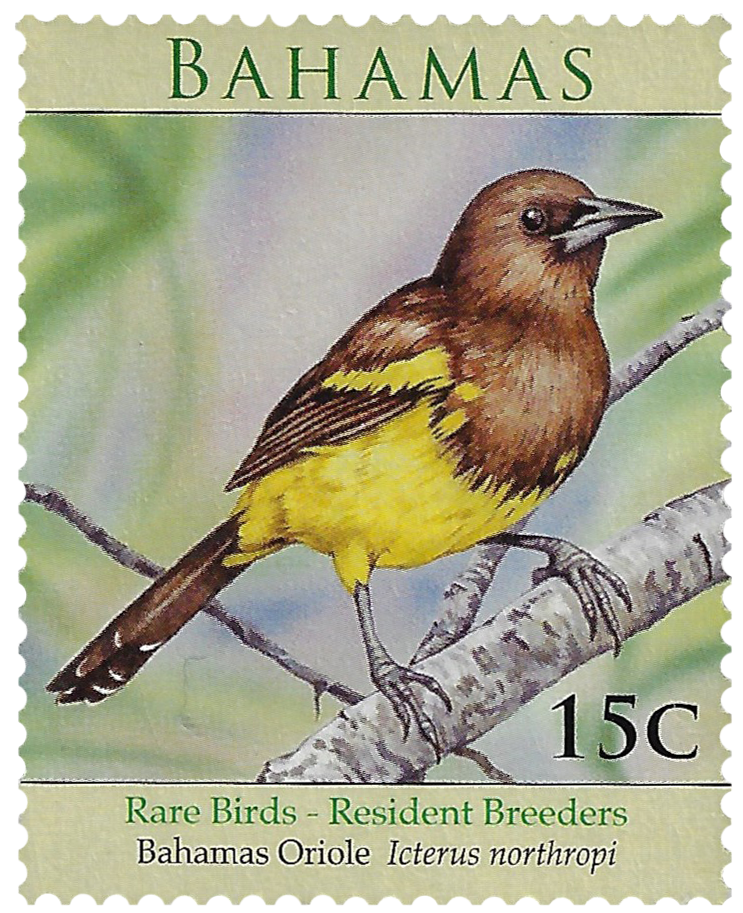
Birds
Some 250 species of birds can be found in the Bahamas. The national bird of the Bahamas is the flamingo. Andros and Inagua are the principal breeding grounds.
Learn more about the Birds of the Bahamas – The Amazing Birds of the Bahamas and BirdsCaribbean
Animals
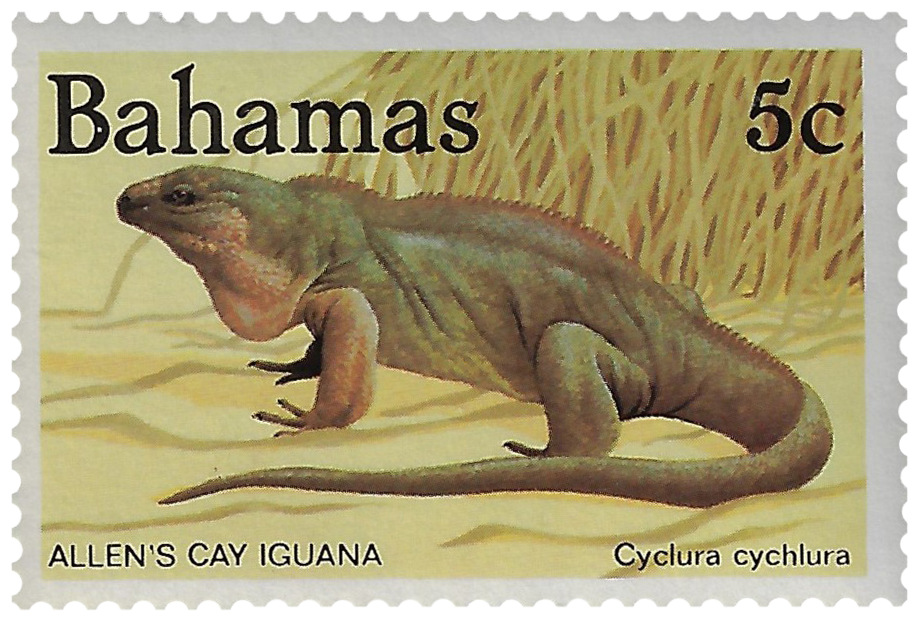
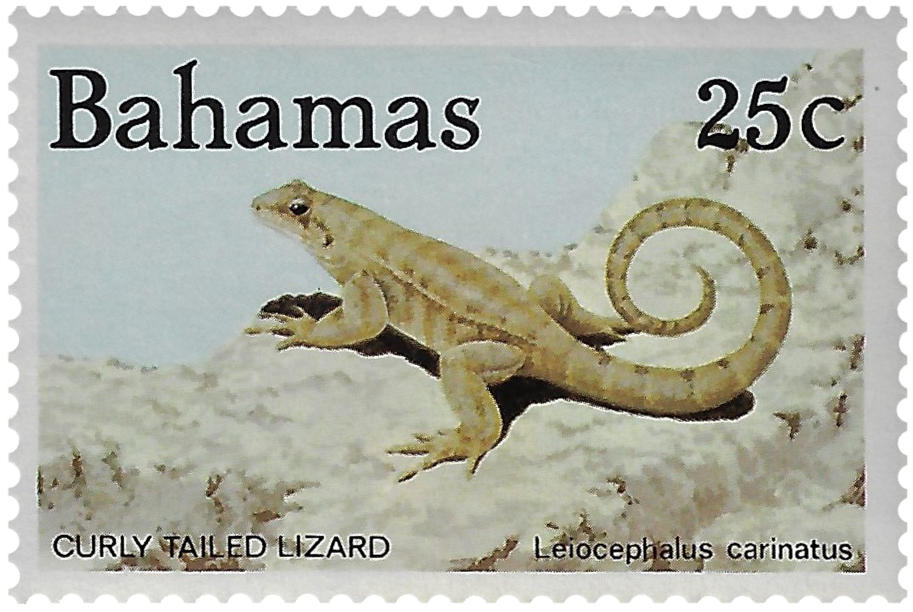
Animal life include racoon, iguanas, lizards, land crabs a few snake species and tree frogs.
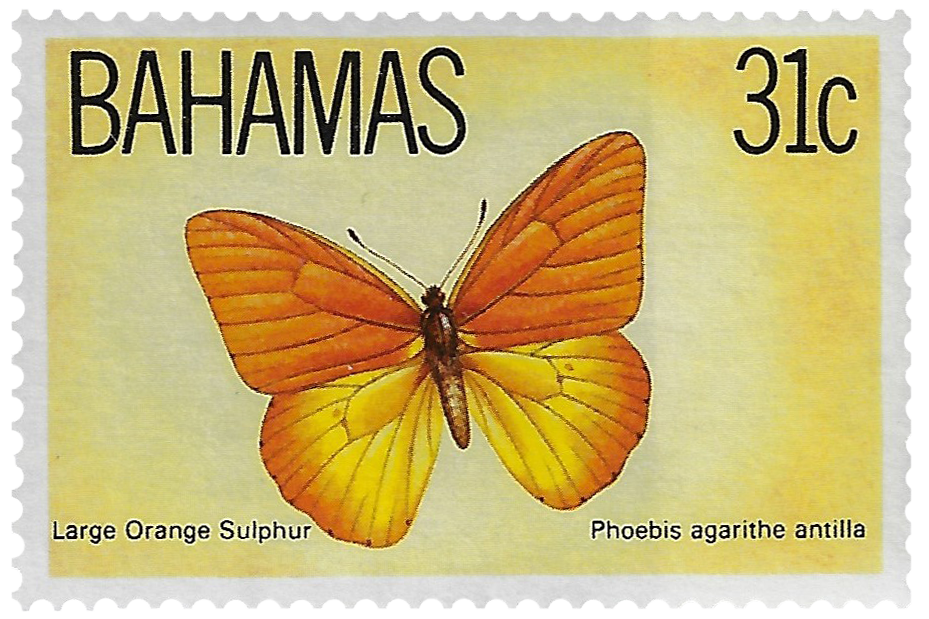
Insects
There are currently 84 butterflies recorded in the Bahamas but there is limited record of the moth variety and population Bahamian Lepidoptera most likely originated from Florida, Central America and the West Indies, especially Cuba and Hispaniola.
Marine Life
Marine life abounds on the Bahama banks and in the surrounding ocean. Fishing is both a popular sport and a means of livelihood. Most of the world's top game fish are found in Bahamian waters, such as marlin, swordfish, tarpon, tuna, wahoo and grouper. The Blue Marlin is the National Fish of the Bahamas and appears in the national shield.
A whole industry has grown around sportfishing for the elusive bonefish.
Learn more about bonefish – Bahamian Fishers Ecological Knowledge Research Initiative
Scale fish in the seas surrounding the Bahamas can be divided into pelagic fish of the Gulf Stream and reef fish, the colorful but smaller fish of the Bahama Banks.
Learn more about the Coral Reef Ecosystems of the Bahamas – Coral Reef
Of the 183 varieties of fish found in Bahamian waters, forty-two varieties are important as food fishes and another twenty-four are edible. Main edible varieties include snapper, grouper, pompano, mahimahi, grunt, jack, runner, porgie, mullet, hogfish, muttonfish, tang turbot, shellfish and tuna.
The Bahamas is considered the shark diving capital of the world with a wide diversity of species.
Learn more about sharks – The Bahamas: Shark Diving Capital of the World
Whales, dolphins and manatees can also be found in Bahamian waters.
The Bahamas Spiny Lobster is the major fish export, with a fishing season from August to March. In 2017, exports of fish and fishery products amounted to USD 87.7 million.
Sponging was once the basis of island economy but the industry was devastated by disease in 1936. There is currently a movement to revitalize the sponging industry.
Read more about sponging: Sponge Fisheries of the Bahamas - Scientific American, November 21, 1981 and Sponging project moves into final phase as spongers ready to revitalize industry nationwide
Three main types of turtle can be found: green turtle, loggerhead turtle and the endangered Hawksbill turtle. All can be found in creek and shoal waters off all the islands.
View swimming with Hawksbill turtle – Shallow water Turtles & Starfish in the BAHAMAS
Read more about endangered Hawksbill turtles – Hawksbill Facts
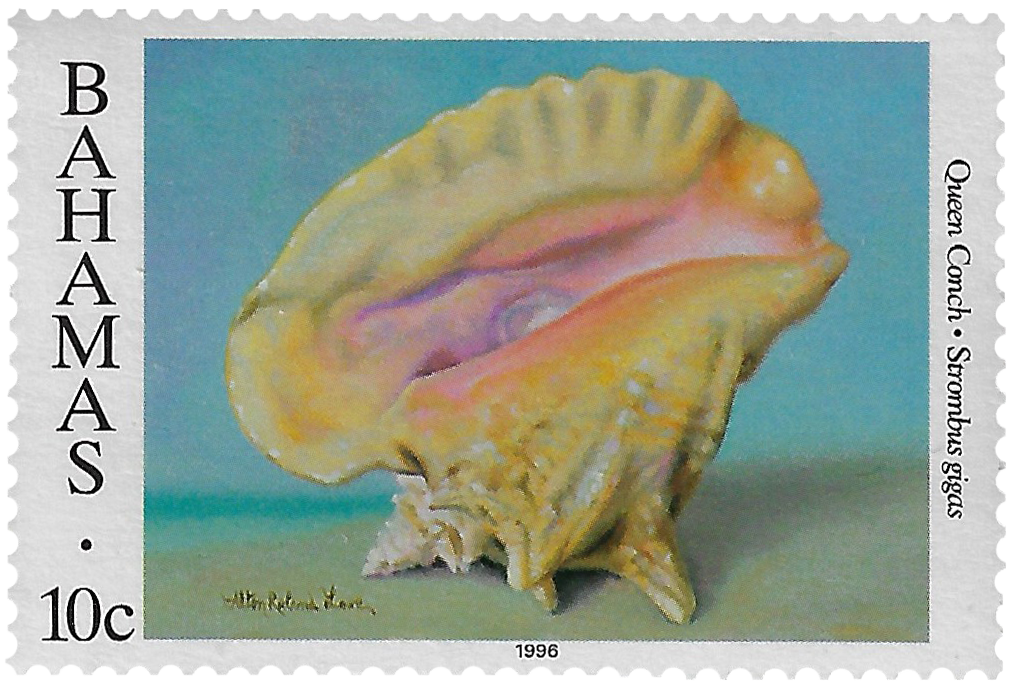
The Queen Conch is part of the staple diet of islanders, but is currently under stress due to overfishing. It’s importance to Island economy was first recognized with the issuance of 1965 stamp by the British Colonial Government.
Shell collecting is a popular shoreline activity.
Plant Life
Vegetation of the Bahamas is similar to that found in other tropical and subtropical islands but many of the principal crops and plants have been imported and are not indigenous.
On forested land on larger islands like Abaco, Andros and Grand Bahama, commercial timber includes pine, lignum vitae, braziletto, logwood, cedar, madeira, sabica and satinwood. The Lignum Vitae (Guaiacum sanctum), also known as ironwood, is the national tree of the Bahamas.
Learn more about the Pine Forests of Grand Bahama – Pine Forest
Prevailing southerly winds and currents have assisted the spread of plants from the southern continent and many seed-eating birds from the north spend their winters in the Bahamas or stop there in migration, depositing seeds carried in flight.
Trees of the Islands
The main variety of palm trees are Palmetto, Goat-palm, Coconut and Silver Thatch. Apart from the provision of food, these palms historically provided material for the thatching of roofs and the crafting of baskets, mats and fish traps. With the passage of time this formed the basis of a cottage industry in straw products. Over a thousand people are employed throughout the islands in stripping fronds from trees, plaiting and weaving them into strips and making hats, purses and baskets which are sold, mainly to tourists.
The Bahama Pine is found in abundance on Grand Bahama. Pinus Bahamensis usually doesn’t exceed eight inches in trunk diameter and seldom reaches a height of more than 35 feet. This tree was harvested for commercial use beginning in the 1930’s. Timber was sawn into planks by local mills for construction of homes and exported throughout the Caribbean. As the supply of mature trees diminished, smaller trees were harvested for export to Europe as pit props in the coal mining industry.
The yellow elder (Tecoma stans) is the National Flower of the Bahamas. Native to Central and South America, it was brought to The Bahamas where it has flourished in the warm climate. The tree blooms between October and December, displaying trumpet-shaped, vivid yellow flowers.
The royal poinciana (Delonix regia) are also known as “flame” trees. Umbrella-like in shape, the tree can grow up to 40 feet in height and bears scarlet blooms from May through September. The tree, which takes its name from M de Poinci, the 17th-century governor of the French Antilles, is originally native to Madagascar, where it is considered an endangered species.
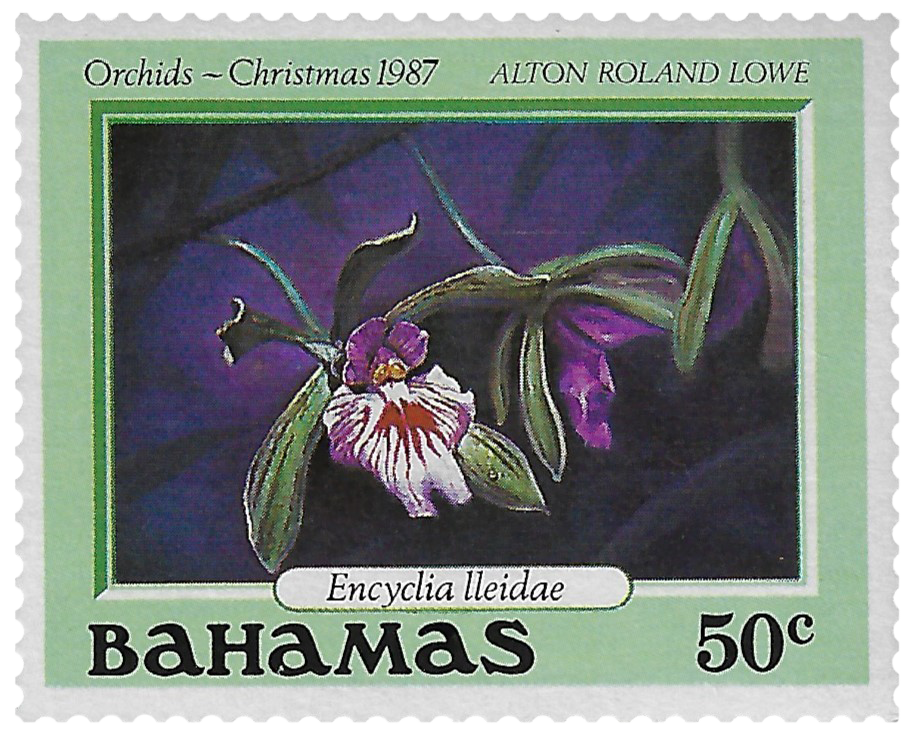
Flowers of the Islands
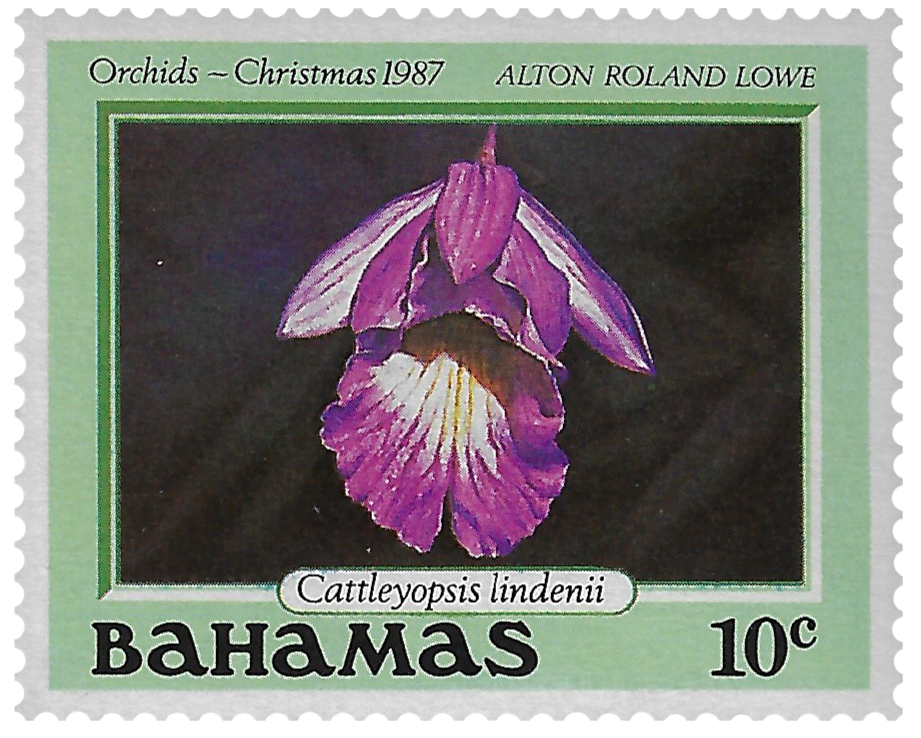
Many species of orchids grow in the islands of the Bahamas. Vanilla is a native, flowering, climbing plant that grows in Blackland Coppice forest. This forest is a humid habitat sheltered by hardwood trees. Purple orchids grow in the pine forest.
Learn more about the flora of the Bahamas – Flora of The Bahamas